What is the difference between a ketogenic diet and a low-carb diet?
In this post, I will outline the most common types of low-carb diets and explain how they differ in terms of carbohydrate allowance and benefits. The Ketogenic Diet is the most low-carb of these diets. Read on to discover other variations of the diet and which one is best for you.
1. Classic Ketogenic Diet
The main difference between a ketogenic diet and a low-carb diet is that a ketogenic diet has the lowest carbohydrate allowance. It is the original form of the ketogenic diet and is also the most restrictive. It is a high-fat, low-carb and moderate protein diet. The diet limits net carbs (total carbohydrates less fiber) to 20g per day. This means that most foods eaten should contain close to zero carbohydrates, to stay within the 20g of net carbs.
Weight Loss
This form of the diet is typically used for weight-loss and to control seizures in children with drug resistant epilepsy. It is quite difficult to follow over a long period, purely because it is so restrictive. Having said that, it is very effective for weight loss. Many people move to one of the modified versions of the ketogenic diet (below) once they have achieved their goal weight.

Many athletes use the Ketogenic Diet to enhance performance. If you’d like to know more, see this post by Patricia Daly.
2. Low-Carb or Modified Ketogenic or Modified Atkins Diet
The Modified Ketogenic Diet is also known as a Modified Atkins Diet. It is what people usually mean when they talk about a “low-carb” diet. This is the less restrictive version of the ketogenic diet where the carbohydrate allowance is slightly relaxed to 40-60g net carbs per day.
Weight Maintenance
A Modified Ketogenic Diet is the natural progression for someone who has lost weight and is looking to maintain their weight, while keeping all the benefits of low-carb eating. These benefits include blood glucose control, appetite suppression, mental performance enhancement, weight control and lower inflammation etc.
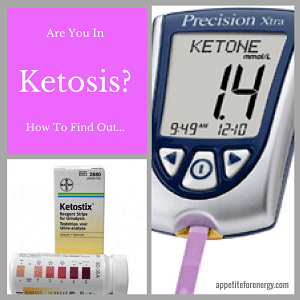
On this diet, a person would generally be in nutritional ketosis* (burning fat instead of glucose) but may fluctuate in and out depending on the individual. You don’t necessarily need to be in continual ketosis to enjoy the benefits described above.
*Nutritional ketosis is where ketones are between 0.5 and 3.0mmol/L.
To learn about how to test for ketosis, see our post on 3 way to test for ketosis.
3. Supplemented Ketogenic Diet – MCT Oil
A Supplemented Ketogenic Diet is similar to the Low-Carb or Modified Atkins Diet with the addition of MCT oil (medium chain triglycerides). The purpose of supplementing the diet with MCT oil (or exogenous ketones) is that more carbohydrate and protein can be consumed while staying in ketosis. The net carbohydrate allowance is 40-60g. The addition of the MCT oil should ensure that you stay constantly in ketosis while enjoying a few more carbs.
How To Take MCT Oil

For some ideas on how to incorporate MCT oils into your diet, see our post on 10 Low-Carb Pantry Essentials.
Exogenous Ketones
Exogenous ketones are ketones that come in powdered form. The easiest way to take them is to mix with water, coffee, almond milk etc and drink. They are quite powerful and will put your body into ketosis quite quickly, often within 10 minutes. They can be useful when transitioning to a ketogenic diet as they provide the body with ketones for fuel before they are produced naturally. It can help minimize keto flu while the body and brain is going through carbohydrate withdrawal. The only downside is that they are expensive.
I find it useful to have exogenous ketones such as Perfect Keto Base (in chocolate!) on hand and use occasionally in the morning after having a carb heavy meal the night before. It gets you back on track and into ketosis quickly without the carb cravings.
As with a Classic Ketogenic Diet, women may find that they need to increase carbohydrates once or twice per week to maintain their hormone levels. This is called a “carb re-feed” or “carb up”. Add up to 30g of net carbs to the evening meal once or twice per week. Men can also include a carb re-feed once per week.
4. Intermittent Fasting Low-Carb Diet

Start your day with Intermittent Fasting or Fat Fasting. This means not eating breakfast or food, only drinking butter coffee or tea until around 2pm. The eating window is 8 hours say from 2pm – 10pm. You can use any 8 hour window that suits your schedule, but this timing is quite common. Eat lunch and dinner within these hours so that you get a 16 hour fast.
Fat Fasting
I find it very difficult to have nothing at all during the fast so I drink butter coffee or bulletproof coffee in the morning. This keeps me satiated till 2pm or later. Drinking butter coffee or tea in the morning without food is known as Fat Fasting or Bulletproof Intermittent Fasting. As only fats are consumed (not carbs and protein), you don’t feel hungry. You get to experience mild levels of ketosis during the day and then eat a low-carb late lunch followed by a carb re-feed at dinner. This could include up to 80g of net carbs. Having the carbs in the evening helps with sleep as it provides the brain with fuel. You will come out of ketosis after the evening meal and then return to ketosis the next morning.
Everyone responds in different ways so you will need to experiment with carb levels and work out how much you can have and still get back into ketosis the next morning. (Assuming that is your goal).
This version allows an even higher carbohydrate allowance while still being in ketosis some of the time.
To learn how to start intermittent fasting, see this post : Step-By-Step Adaptation Guide To Intermittent Fasting.
5. Cyclical Ketogenic Diet – Advanced Diet

I have never tried this but if you are interested to learn more, click here.
What Is The Difference Between A ketogenic Diet And A Low-Carb Diet?
| Classic Ketogenic Diet2 | Modified Atkins or Modified Ketogenic or Low-Carb Diet | Supplemented Keto Diet (MCT oil) | Intermittent Fasting Keto Diet | Cyclical Keto Diet | |
| Description | The original high-fat, low-carb, moderate protein diet. Most restrictive of the low-carb diets and most difficult to follow. | As per the Classic Keto Diet but more carbs (and protein), less fat, | As per the Classic Keto Diet but more carbs (and protein), less fat and supplementing with MCT oil. | As per the Classic Keto Diet but adding intermittent fasting or fat fasting & more carbs and protein | 5-6 days of the Classic Keto Diet followed by 1 or 2 days of high carbohydrate eating. |
| Net Carbs1 per day | 20g | 40-60g | 40-60g | 40-100g | 30g on 5-6 days
60-70% of total calories on carb days |
| Protein per day | 10% of diet by calories | 20-25% of diet by calories | 20-25% of diet by calories | 20-25% of diet by calories | Varies. |
| Time in Ketosis 4 | Continuous | May fluctuate in and out of ketosis | Continuous | Will come in and out of ketosis during a 24 hr period | Yes on keto days and no on carb days |
| Modifications | Women may need to “re-feed”³ carbs a couple of times per week and men once per week. | Women may need to “re-feed”3 carbs a couple of times per week and men once per week. | Women may need to “re-feed”3 carbs a couple of times per week and men once per week. | ||
| Used For 5 | Epilepsy seizures , major weight loss, blood glucose control for diabetes. Medically supervision is required. | Weight loss and maintenance, blood glucose control etc | Weight loss and maintenance, blood glucose control etc | Weight loss and maintenance, blood glucose control etc | Maximize muscle growth and training performance |
Notes
- Net carbs are total carbohydrates less fiber
- The Classic Ketogenic Diet is not recommended for children (except those with drug resistant epilepsy under medical supervison), teens or people in their 20’s with good insulin sensitivity in general.
- A carb re-feed is where you consume up to 30g of additional carbs at the evening meal. This helps to balance out hormone levels
- This is a guide only. Individuals would need to test their ketone levels to ensure they are achieving ketosis on any given level of carbs/protein. Other factors such as exercise intensity levels will also play a role. Nutritional ketosis is defined as ketone levels between 0.5 and 3.0 mmol/L.
- Note that individual results will vary especially for weight loss, blood glucose control. They will depend on other factors such as calories consumed and exercise level.
I hope this post helped to explain the difference between a ketogenic diet and a low-carb diet. If you have any questions or thoughts, please leave a comment below. We’d love to hear about your experience with the different versions of the ketogenic diet.
Get FREE 30-Minute Low-Carb Recipes
You'll also receive our FREE 100 Ketogenic Foods List PDF
This post contains affiliate links which means I may receive a small commission if you purchase some items. Ordering through my site will not change the price you pay. Small commissions like this help to support this blog and my bulletproof coffee habit…
FREE KETO FAST-START GUIDE FOR BUSY MUMS WITH 3-DAY MEAL PLAN
Start burning fat in 3 Days without cooking 2 meals OR going HUNGRY!
You'll also receive FREE 30-minute keto recipes, training and our updates via email.
Read our Privacy Policy here






 One Pan, 30 Minute – Chicken, Parmesan And Zoodle Skillet
One Pan, 30 Minute – Chicken, Parmesan And Zoodle Skillet


Great article. Very helpful. Thank you!
Thanks for the feedback and I’m glad you found it helpful!