Low-carb diet weight loss has been the subject of much discussion in recent times. The question being asked is, what substance is there behind all the hype?
Indeed, studies¹ have shown that you can lose twice as much weight on a low-carb diet compared to a low-fat diet.
In this post, we take a look at why and how the low-carb diet works for weight loss.
How does it turn your body into a fat burning machine? And how is it different to a low-fat diet? Many people are attracted to eating low-carb because it is completely different to many other “diets” out there.
There has been a lot of scientific studies done to understand how and why the keto way of eating works for fat burning. It turns our current low-fat, low-calorie thinking on its head.
How is the low-carb diet different?
The low-carb diet involves a fundamental change in the way your body is fuelled. Your body switches from using carbohydrates or glucose for fuel, to using fat.
It’s pretty amazing that your body can switch fuel pathways. We have always had this ability, but most of us will never use it in our entire lifetime. The origin of this ability goes right back to the days when humans did not always have enough food to eat and often had to go for days or weeks without food.
There are 7 reasons why the low-carb or ketogenic diet makes losing weight easy. Some reasons are physical and others affect your motivation. Read on to learn more…
Why does the low-carb diet work for weight loss?
- Your body goes into nutritional ketosis and learns to burn fat
- Appetite is suppressed
- Fewer calories are naturally consumed
- Higher protein reduces appetite and maintains muscle mass
- There are many other positive health benefits e.g. insulin control
- Initial weight loss is rapid, increasing motivation
- The restrictive nature of the diet actually reduces cravings
There are 4 physical reasons why the low-carb approach works for weight loss
1. Your body goes into nutritional ketosis and learns to burn fat
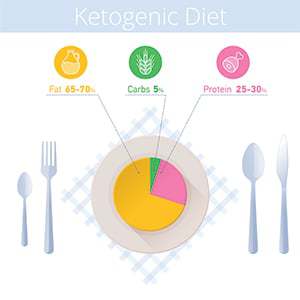
The Low-Carb Diet involves eating a diet that is high in fat, moderate in protein and low in carbohydrate (sugars and starch). The result of eating this way is that the body switches from burning glucose (sugar or glycogen) for energy to burning fat.
The reduction in carbs in the diet flips a switch that turns on the body’s preference for burning fat for fuel. The body will choose to burn carbs or glycogen when they are present, before using fat as fuel. The drop in carbs in the diet is the critical factor in flipping this switch to tell your body to burn fat.
For more info on how to start a low-carb or ketogenic diet:
5 Tips For Getting Started on a Low-Carb Diet
How does ketosis work?
Initially, you’ll burn through the stores of glycogen (sugar stored in the body) before fat burning starts. This is usually the most challenging part of starting a low-carb diet, but once this happens, weight loss magically starts to happen. Of course, this is far from magic and is a well-studied biological process. However, when you start to lose weight quickly and steadily, without starving yourself, it does seem like magic.
When the body starts to burn fat instead of carbohydrate for energy, your body goes into a metabolic state known as nutritional ketosis.
Stubborn fat that you’ve struggled to lose for years, starts to disappear.
The longer you stay on a low-carb diet though, the better you get at this process of fat burning. You become what’s known as fat-adapted and this means that your body can easily switch between using carbs or fat as fuel, without the unpleasant keto flu side effects you initially experience. If you fall off the keto wagon, this makes it easier to get back on.
Essentially, your body learns to become highly efficient at burning fat for energy instead of carbohydrates.
What about the cavemen?
Many, many years ago, when hunters couldn’t find food for days or weeks, their bodies would go into nutritional ketosis and use their body fat as fuel, while they waited for their next successful hunt.
The human race would never have survived without this primitive ability to go without food. The ability to switch fuel pathways is rarely used today in the western world but is available to anyone who pursues a low-carb diet.
You don’t have to fast to achieve this effect – simply eating a very low-carb diet (20-50g net carbs per day), switches on the fat burning pathway.
2. Appetite is suppressed
Food cravings are the most frequently cited reason for failing to stick to a diet in studies, so listen up!
The second key reason that ketogenic diets are successful for weight loss is due to the appetite suppressing effect. Appetite suppression is caused by nutritional ketosis and the satiating effects of a higher fat diet.
Being in a state of nutritional ketosis, (where the body starts to burn fat instead of carbohydrate for energy), has been shown to reduce hunger.
When eating a low-carb, high-fat diet, the high-fat content of meals actually slows gastric emptying. This means that food passes through your gut at a slower speed and you feel satiated for longer.
A 2-year study found that a low-carb diet promoted satiety. Those on the low-carb diet were less bothered by hunger than people on the low-fat diet in the study over 2 years.
Are you maintaining your weight?
For those maintaining their weight, it is quite difficult to eat enough calories to actually gain weight. So a low-carb diet is excellent for keeping the weight off once you’ve lost it.
Many people continue to eat this way for this reason, as well as the many health benefits that come with a keto lifestyle such as insulin control, improved cardiovascular factors, and mental clarity.
How does appetite suppression on a ketogenic diet help with weight loss?
- Fewer calories are consumed (compared to a low-fat diet, where you don’t experience a subdued appetite)
- The lower calories consumed contribute to weight loss
- The mind is not focussed on food all the time
3. Fewer calories are naturally consumed
As discussed above, one of the most common benefits low-carb dieters report is feeling much less hungry than usual. Reduced hunger leads to fewer calories being consumed.
This is one of the key factors that set the keto diet apart from the low-fat diet and many others.
On a low-fat diet, typically calories are restricted to 1200-1500 k/cal per day for women and 1500-1800 k/cal per day for men. The keto diet usually does not restrict calories and dieters can eat until they are full.
The result of this is that those following a low-fat diet usually report suffering from extreme hunger and require supreme willpower to stay on track with the diet.
Those on a low-carb, high-fat diet, report higher levels of satiety and appetite suppression. As they are not as hungry, this helps them to stay on track with the diet and lose weight.
Further to this, the reduced hunger leads to fewer calories being consumed and more weight loss.
The process of weight loss on a low-carb diet:
- Carbohydrates are reduced in the diet
- The body burns off existing sugar stores in the body (glycogen)
- A state of nutritional ketosis begins (where the body relies on fat as fuel, not glucose)
- Nutritional ketosis causes appetite suppression
- Appetite suppression leads to lower consumption of food and therefore calories
- The combination of the body burning fat for fuel (not carbs) and reduced calories leads to…
- Weight loss and reduction of body fat
4. Higher protein reduces appetite and maintains muscle mass
Once carbohydrates are removed from the diet, protein tends to form a higher proportion of the diet compared to a low-fat diet.
Higher protein is also thought to contribute to reduced appetite and helps to maintain muscle mass. Maintaining muscle mass allows calories to be burnt at the same level and prevents the rate of calorie burn from falling due to muscle wastage.
This study found that a low-carb diet was protective against muscle protein catabolism.
Protein is good but don’t overdo it…
While protein forms a higher proportion of the diet compared a low-fat diet, it is important not to eat too much protein.
Keep in mind that a low-carb/ketogenic diet is defined as a low-carb, high-fat and moderate protein diet.
Around 20% of your diet (by calorie) should be protein. This is somewhere between 90-150g per day or 1-1.5 g of protein per kg of body weight per day
The reason to limit protein is that excess protein is converted into glucose in the body in a process known as gluconeogenesis.
The extra glucose in the body will kick you out of ketosis!
To learn more, read our article on How Much Protein Should I Eat On A Ketogenic Diet?
In summary, higher protein contributes to reduced appetite and helps to maintain muscle mass.
There are also powerful psychological reasons why low-carb diets work for weight loss
5. There are many other positive health benefits e.g. insulin control
Benefits such as insulin control, improved cholesterol, lower triglycerides and improved mental clarity mean that people stay on the diet for longer periods of time. The many health benefits drive motivation to stay on track and maintain steady weight loss.
When you are losing weight but also improving your health, you will tend to be highly motivated to continue.
Here are just some of the positive health benefits apart from weight loss;
- reduced blood glucose
- lower triglycerides
- improved cholesterol – increased HDL “good” cholesterol, reduced LDL “bad” cholesterol
- improved reflux
- fertility & PCOS
- improved acne
- reduced inflammation (flat belly)
- mental clarity
- more energy
In summary, there is a multitude of health benefits to be enjoyed on a keto diet from lowered blood glucose to improved mental clarity.
6. Initial weight loss is rapid, increasing motivation
People can lose up to 10 pounds (4.5 kilos) in the first 10 days, but more commonly 3-6 pounds (2 kilos).
While a large part of this is water loss, because the body sheds water as a result of the drop in insulin and glycogen levels, it does provide a huge motivation for people to continue on.
You’re losing weight, your tummy is shrinking and you are feeling great. The weight loss will naturally slow to a more stable level of 1-2 pounds per week, however, you’ll feel highly motivated because it’s working.
This importance of motivation can’t be underestimated as a reason for why people stay on a low-carb diet and hence why they work, particularly for weight loss.
7. The restrictive nature of low-carb diets reduce cravings
As the ketogenic diet is very restrictive, there is less food choice and this, in turn, leads to people eating less and consuming fewer calories.
It is often thought that a very restrictive diet would lead to increased cravings for those foods, however, studies have shown that the opposite is true.
A 2-year study that looked at food cravings, food preferences and appetite found that those on a low-carb diet had “significantly larger decreases in cravings for carbohydrates/starches and preferences for high-carbohydrate and high-sugar foods”.
So actually, following a restrictive diet reduced cravings for carbohydrates like bread, pasta, pizza, and donuts.
We actually get used to not eating these foods and enjoy the foods that are available to us.
Interestingly, the strict nature of a low-carb diet actually makes it easier to stick to over the long-term and achieve your weight loss goals.
For lots of FREE information about starting a low-carb diet, check out our Essential Guide To Starting A Low-Carb Diet where you’ll find everything you need to know to start today!
If you enjoyed this article, please leave a comment below!
Get FREE 30-Minute Low-Carb Recipes
You'll also receive our FREE 100 Ketogenic Foods List PDF
More studies on low-carb diet weight loss:
- Brehm BJ, Seeley RJ, Daniels SR, D’Alessio DA. A randomized trial comparing a very low carbohydrate diet and a calorie-restricted low fat diet on body weight and cardiovascular risk factors in healthy women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:1617–1623.
- Samaha FF, Iqbal N, Seshadri P, et al. A low-carbohydrate as compared with a low-fat diet in severe obesity. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:2074–2081.
- Yancy WS, Jr, Olsen MK, Guyton JR, Bakst RP, Westman EC. A low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet versus a low-fat diet to treat obesity and hyperlipidemia: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140:769–777.
FREE KETO FAST-START GUIDE FOR BUSY MUMS WITH 3-DAY MEAL PLAN
Start burning fat in 3 Days without cooking 2 meals OR going HUNGRY!
You'll also receive FREE 30-minute keto recipes, training and our updates via email.
Read our Privacy Policy here












 Low-Carb Mint Chocolate Strawberry Fat Bombs
Low-Carb Mint Chocolate Strawberry Fat Bombs

